
Since r+g+b=1, the chromaticity can be represented using only 2 values (r & g). Below is the normalized chromaticity space (x-axis is r and y-axis is g).

We now proceed with picking out the ROI. There are two methods: the Parametric and the Non Parametric.
Parametric
In this method, we first crop a subregion in the ROI. From this patch, we take the mean and standard deviation of r and g. We then compute for the distribution probability (we assume a Gaussian) using:

We do the same for p(g). The joint probability is just the product p(r)p(g). Below are sample the results:

Original Image

Parametric
ROI: Blue Tiles

Parametric
ROI: Yellow Tiles
Non Parametric (Histogram Backprojection)
In this method, we take the 2D r-g histogram of the crop subregion of the ROI. We then backproject the value to the pixel location of the original image. Below are sample the results:

Original Image

Parametric
ROI: Blue Tiles

Parametric
ROI: Yellow Tiles
Comparing between the two method, we could observe that the Parametric method has a better result.

Original Image

Parametric
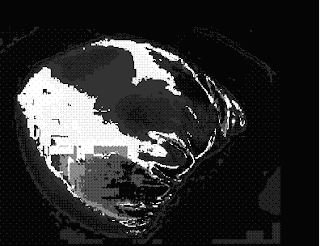
Non Parametric
I've successfully accomplished the activity. I want to give myself a 10.
No comments:
Post a Comment